HIV Symptoms in Women: A Comprehensive Guide with Pictures
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a global health concern that affects millions of people worldwide. While both men and women can contract HIV, the virus can manifest differently in each gender. Understanding the specific symptoms of HIV in women is crucial for early detection, treatment, and prevention. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the common symptoms of HIV in women, along with relevant pictures to help you recognize potential signs.
Understanding HIV in Women:
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, which are responsible for fighting off infections and diseases. When left untreated, HIV can progress to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), which is the final stage of the infection. While there is no cure for HIV, early diagnosis and proper treatment can help manage the virus effectively and prevent its progression.
It is important to note that not all individuals infected with HIV will exhibit the same symptoms, and in some cases, symptoms may not appear for years after contracting the virus. However, understanding the potential signs can help individuals seek medical attention and get tested for HIV.
Common Symptoms of HIV in Women:
1. Flu-like Symptoms: Many individuals experience flu-like symptoms within 2-4 weeks after contracting HIV. These symptoms may include fever, fatigue, swollen glands, sore throat, and body aches. While these symptoms are not specific to HIV, they should not be ignored, especially if there is a known risk of exposure.
2. Skin Rashes: Skin rashes are a common symptom of HIV. These rashes may appear as small, red bumps or as larger, patchy areas. They can be itchy, painful, and may appear on various parts of the body.
3. Recurrent Infections: Women with HIV may experience frequent and persistent infections, such as vaginal yeast infections, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). These infections can be more severe and difficult to treat in individuals with weakened immune systems.
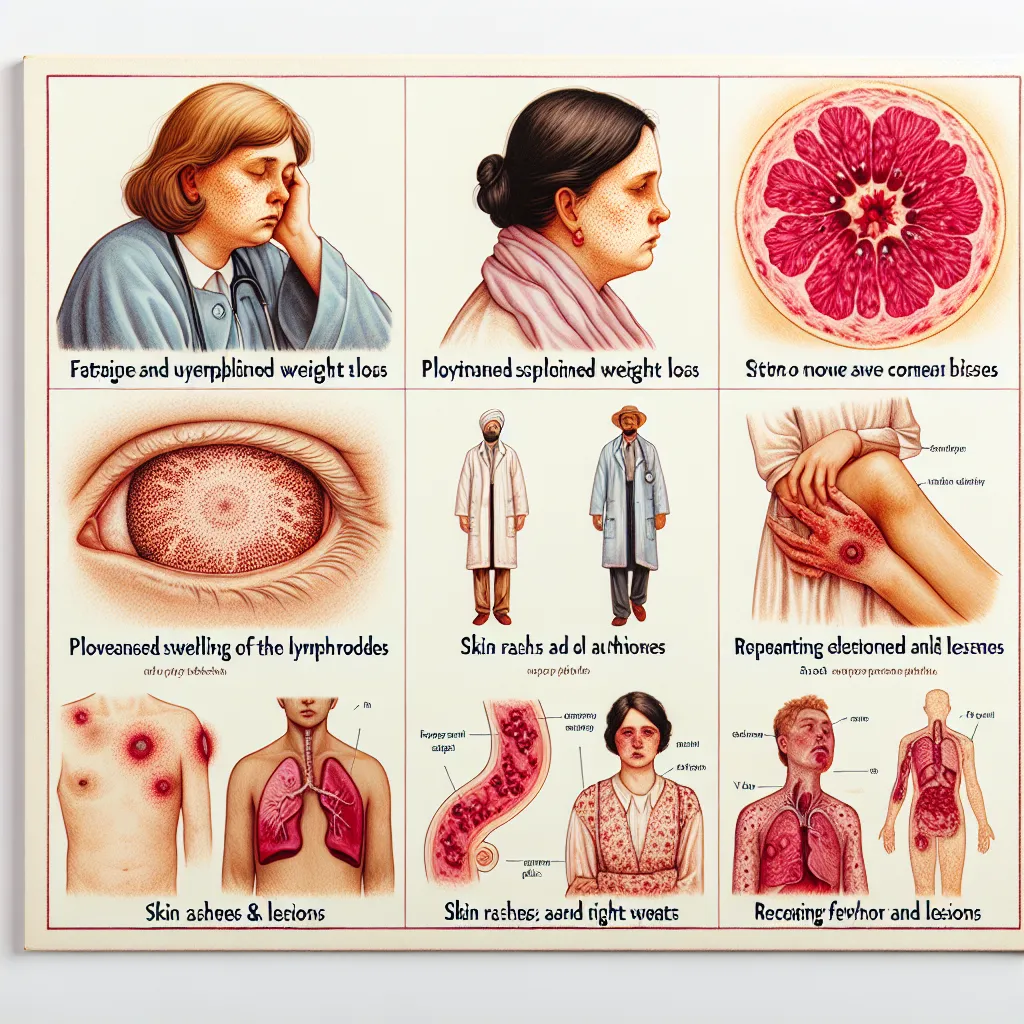
4. Menstrual Irregularities: HIV can affect the menstrual cycle in women, leading to irregular periods, heavier or lighter flows, and more severe premenstrual symptoms. These changes can occur even in women with previously regular cycles.
5. Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss is a common symptom of HIV. Women may experience a significant decrease in appetite, leading to weight loss and malnutrition. This symptom can often be accompanied by chronic diarrhea and digestive issues.
Pictures of HIV Symptoms in Women:
It is important to remember that symptoms alone cannot confirm an HIV infection, and the presence of these symptoms does not necessarily indicate HIV. However, being aware of potential signs can be helpful in seeking medical attention and getting tested for HIV. Here are some pictures illustrating common HIV symptoms in women:
Seeking Medical Attention and Testing:
If you suspect that you may have been exposed to HIV or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and provide appropriate guidance and treatment.
HIV testing is the only way to confirm HIV infection. Various testing methods, such as blood tests, saliva tests, and rapid tests, are available to detect the presence of HIV antibodies or the virus itself. It is recommended to get tested regularly, especially if you engage in high-risk behaviors or have multiple sexual partners.
Prevention and Treatment:
Prevention is key in reducing the spread of HIV. Women can protect themselves by practicing safe sex, which includes using condoms consistently and correctly. Additionally, regular testing, open communication with sexual partners, and avoiding shared needles or other drug paraphernalia can help prevent HIV transmission.
While there is no cure for HIV, antiretroviral therapy (ART) can effectively manage the virus, slow its progression, and reduce the risk of transmitting HIV to others. Adhering to prescribed medications, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking regular medical care are crucial for managing HIV.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the symptoms of HIV in women is essential for early detection and timely treatment. While symptoms can vary from person to person, being aware of potential signs and seeking medical attention if needed can make a significant difference in managing the virus and preventing its spread. Remember, getting tested regularly and practicing safe behaviors are key to protecting yourself and others from HIV.